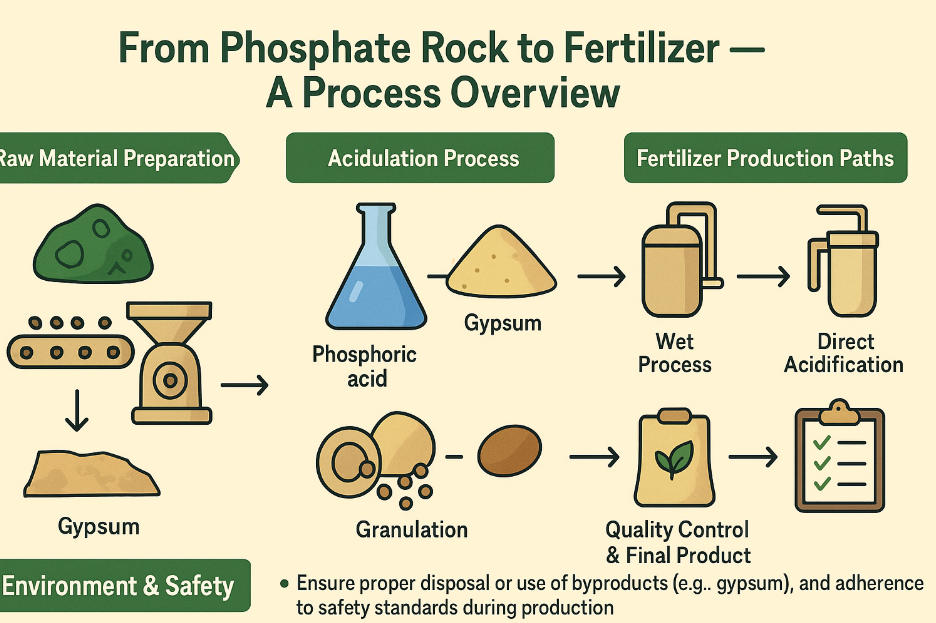
The journey from phosphate rock to fertilizer involves multiple steps that transform raw materials into valuable agricultural products. Here's an outline of the key stages:
1. Raw Material Preparation
Phosphate rock is crushed, ground, and purified to remove impurities.
2. Acidulation Process
Phosphate rock undergoes sulfuric acid treatment, producing phosphoric acid and gypsum.
3. Fertilizer Production Paths
Two main pathways:
a. Wet Process (for producing phosphoric acid used in DAP/MAP)
b. Direct Acidification (for producing single or triple superphosphate)
4. Granulation
The fertilizer mixture is granulated, dried, and cooled to form solid, easy-to-apply fertilizer.
5. Quality Control & Final Product
The fertilizer undergoes strict quality control to ensure it meets agricultural standards.
🌍 Environment & Safety
Ensure proper disposal or use of byproducts (e.g., gypsum), and adherence to safety standards during production.